Greater Lotus
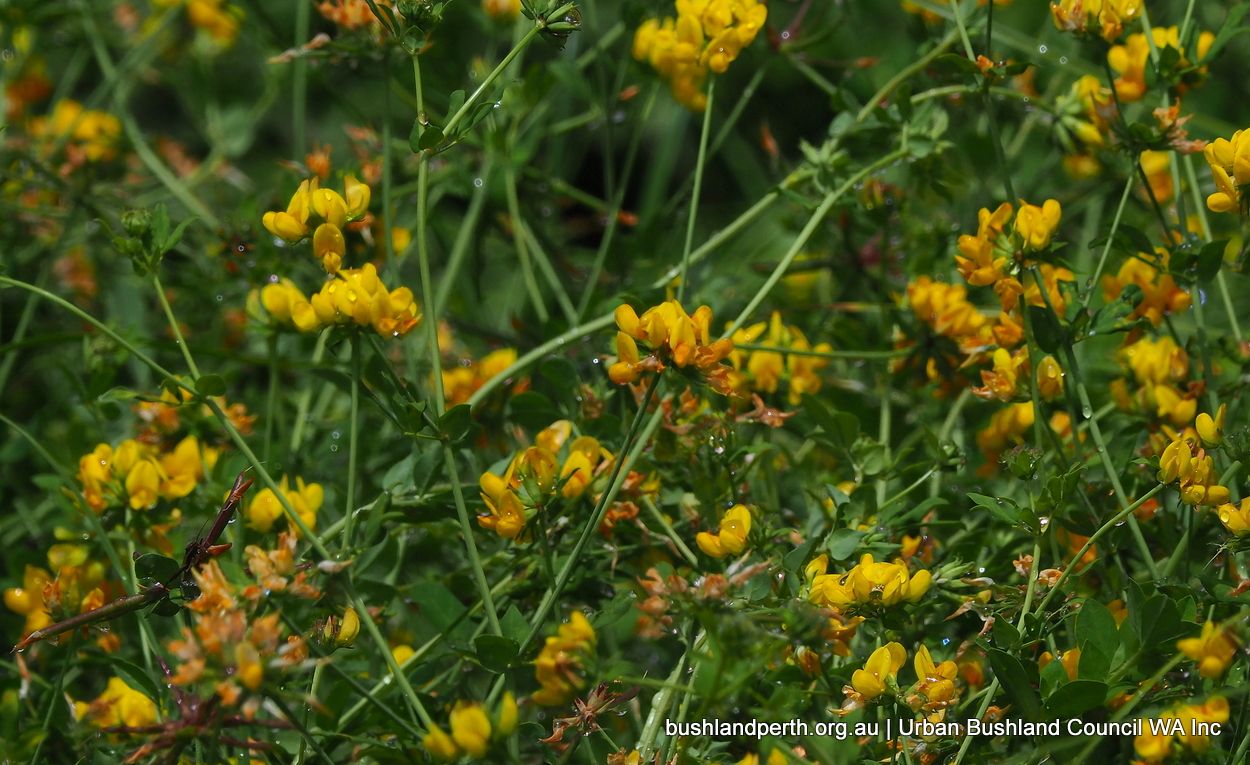
Common name
Greater Lotus
Scientific Name
Lotus uliginosus
Type of plant
Legumes And Peas (Family Fabaceae)
About this weed
Originally from northern Africa and Europe, Greater Lotus has now become naturalised in the US and Australia. It is a weed of cultivated areas and highly disturbed sites, in acidic soils and tolerates water-logging and flooding. It produces yellow pea flowers throughout the summer months. Originally it was introduced as animal forage.
Description
Greater Lotus is an erect or ascending perennial herb, with up to 15 yellow flowers on each head. It is a summer flowering herb and reproduces by seed and rhizomes. Seeds are dispersed by soil and water. Most germination occurs in autumn during warmer temperatures. Fire is unusual in its habitat, however plants survive and resprout from rhizomes.
Impact on Bushland
Rapid rate of spread in native vegetation.
Location
Occurs in the South-West Province in highly disturbed or cultivated sites.
Priority for removal
High: as it may cause acute disruption of ecological processes
Management (hand)
Hand remove small/isolated populations.
Management (herbicide)
Spot spray Lontrel® at 10 ml/10 L + 25 mL wetting agent. Optimum months for herbicide treatment is October through to February. Read the manufacturers’ labels and material safety data sheets before using herbicides. For further information consult the Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority to determine the status of permits for your situation or state.
Flowering month/s
January, February, March, November, December
Flower colour/s
Yellow
Information source
https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/4063
Additional information
https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/weeds/swanweeds/
Hussey, B.M.J., Keighery, G.J., Dodd, J., Lloyd, S.G. and Cousens, R.D. (2007) Western weeds. A guide to the weeds of Western Australia, Second Edition, The Weeds Society of Western Australia, Victoria Park, Western Australia.



